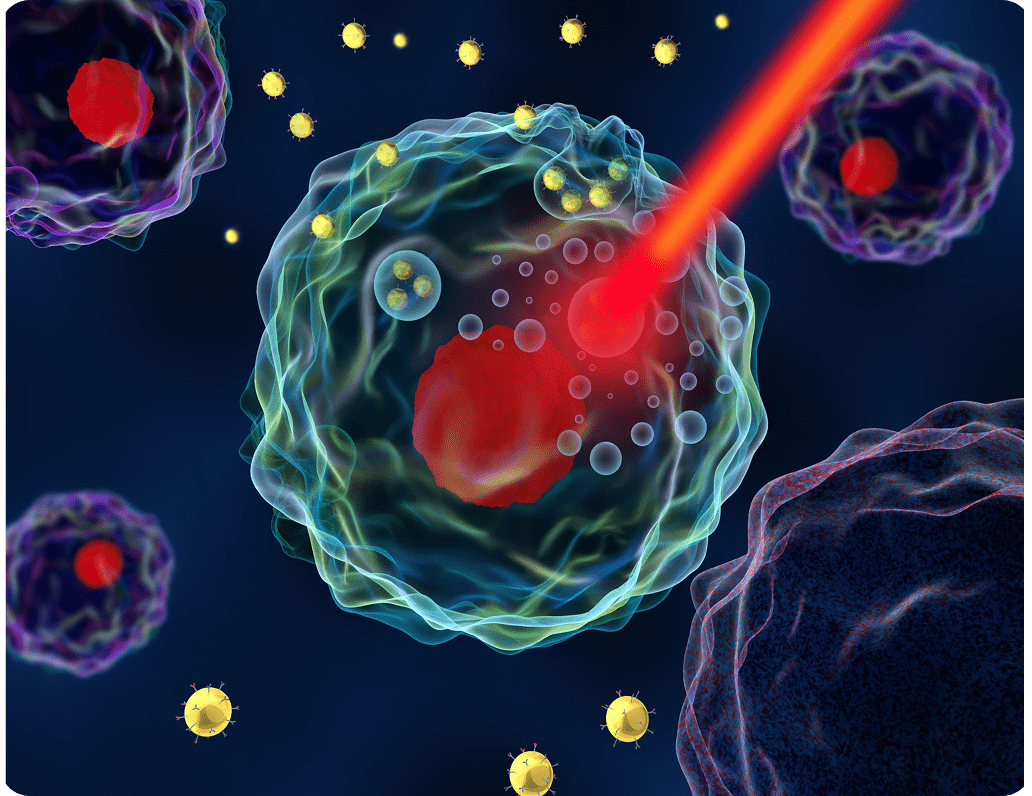
Anti-Inflammatory Effect
Effect of Laser Therapy on the Expression of Inflammatory Mediators… Pubmed
Laser Therapy reduces inflammation with vasodilation, activation of the lymphatic drainage system, and reduction of pro-inflammatory mediators; as a result, inflammation, erythema, bruising, and edema are reduced. This is one of the primary goals in Photomedicine (Laser) Therapy.
Analgesic Effect
Anti-inflammatory and Analgesic Effects of Laser Therapy… Pubmed
Reduction of pain through the suppression of nerve signal transmission over unmyelinated c-fibers; production of high levels of peptides such as endorphins and enkephalins from the brain and adrenal glands, offering successful treatment of many conditions; a suppression of nociceptors, an increase of simulated threshold, an increased release of tissue endorphins.
Accelerated Tissue Repair and Cell Growth
Effect of Laser Therapy on Proliferation and Differentiation of Cells… Pubmed
Photons of light from lasers penetrate deeply into tissue and accelerate cellular reproduction and growth. Laser light increases the energy available to the cells so that they can take on nutrients and get rid of waste products more quickly; perfect for integrative medicine.
Improved Vascular Activity
Blood Flow After Laser Therapy. Pubmed
Laser therapy is purported to improve blood flow in soft tissues. Modulating circulation would promote healing by controlling postinjury ischemia, hypoxia, edema, and secondary tissue damage.
Increased Metabolic Activity
Blood Flow After Laser Therapy. Pubmed
Laser therapy creates higher outputs of specific enzymes, greater oxygen and food particle loads for blood cells.
Trigger Points and Acupuncture Points
Efficacy of Laser Therapy Applied at Acupuncture Points. Pubmed
Laser therapy stimulates muscle trigger points and acupuncture points on a non-invasive basis, providing musculoskeletal pain relief.
Reduced Fibrous Tissue Formation
Muscle regeneration is a complex phenomenon, involving replacement of damaged fibers by new muscle fibers. During this process, there is a tendency to form scar tissue or fibrosis by deposition of collagen that could be detrimental to muscle function. Laser therapy significantly reduced the lesion percentage area in the injured muscle (p<0.05), increased mRNA levels of the transcription factors MyoD and myogenin (p<0.01) and the pro-angiogenic vascular endothelial growth factor (p<0.01). Moreover, Laser Therapy decreased the expression of the profibrotic transforming growth factor TGF-β mRNA (p<0.01) and reduced type I collagen deposition (p<0.01). These results suggest that photomedicine could be an effective therapeutic approach for promoting skeletal muscle regeneration while preventing tissue fibrosis after muscle injury. Pubmed
Improved Nerve Function
Therapeutic laser energy accelerates the process of nerve cell regeneration and increases the amplitude of action potentials to optimize motor and sensory nerve functions, and stimulates the regeneration of myelin and other nerve tissues to decrease pain.
Efficacy of Laser Therapy in Nerve Injury Repair – a New Era in Therapeutic Agents and Regenerative Treatments. Pubmed
Immunoregulation
Laser therapy benefits the immune system by stimulating immunoglobulins and lymphocytes; energy is absorbed by targeted chromophores (molecular enzymes) that react to laser light. The production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) accelerates in targeted tissues, stimulating increased energy for all chemical reactions in targeted cells.
The Potential Role of (Laser Therapy) in Long COVID-19 Patient Rehabilitation. Pubmed
Faster Wound Healing
Laser therapy accelerates the body’s natural healing processes by using stimulated light energy to increase blood flow, reduce pain, accelerate tissue repair, heal wounds, and improve nerve function and vascular activity. Pubmed
Therapeutic lasers heal tissue ailments by pushing billions of photons of invisible laser light deep into the tissues.
Laser therapy ultimately will result in acceleration of pain relief, inflammation reduction and tissue repair. The light energy is absorbed in the cytochromes (receptors of the cell). As a result, the rate of ATP production (cell energy) from the cell is increased – bringing the rate of cell metabolism from a depressed rate, as is the case of damaged tissue, to a normal level. As a result of this increased cell metabolism, many different biological effects may occur. Cell repair is stimulated among all different tissues; tendon, bone, skin, nerve and muscle can all be affected. Laser light has been shown to regenerate nerve cells and